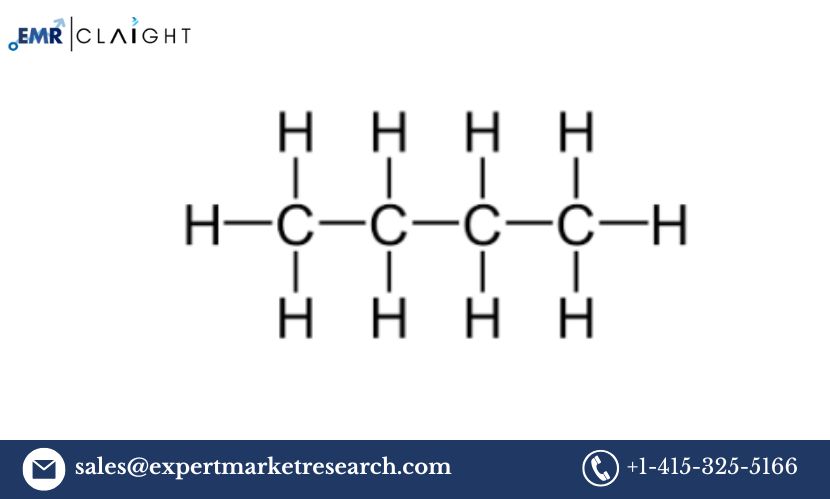
Introduction
The Butane Manufacturing Plant Project Report provides a comprehensive guide for establishing a manufacturing facility dedicated to the production of butane, a highly versatile and essential hydrocarbon. Butane is commonly used in various industries, including as a fuel in lighters, gas stoves, and for the production of synthetic rubber and chemicals. It is also an integral part of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), widely used for domestic and industrial heating and cooking. Given the increasing demand for clean and efficient energy sources, as well as the growth in the chemical and automotive sectors, the establishment of a butane manufacturing plant presents a profitable investment opportunity. This report will delve into the key aspects of setting up a butane manufacturing plant, including market demand, raw material sourcing, production processes, required equipment, workforce requirements, and financial considerations.
Market Demand and Applications of Butane
Butane is a highly sought-after commodity across multiple industries, driven by its extensive applications in energy production, manufacturing, and chemical synthesis. The demand for butane has been steadily rising due to the increasing global reliance on LPG and its use in numerous industrial processes.
1. Energy and Fuel Industry
One of the primary applications of butane is in the LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) industry, where it is blended with propane to produce a fuel source for heating, cooking, and transportation. LPG is widely used as an alternative to traditional fossil fuels in both residential and industrial settings. In particular, butane is used in areas with colder climates because it has a lower boiling point than propane, making it more efficient in low-temperature conditions.
Butane is also utilized in camping gas, portable stoves, and lighters. These uses have driven substantial demand in the retail sector, especially in regions with high outdoor activity rates.
2. Chemical Industry
Butane is used as a raw material in the production of various chemicals, such as butadiene, which is a key component in synthetic rubber and plastics. Butadiene is crucial in the manufacture of tires, adhesives, and elastomers. Additionally, butylene (a derivative of butane) is used in the production of polybutylene, which is used in the manufacturing of pipes, coatings, and other industrial products.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
3. Automotive Industry
Butane is used as an additive in gasoline to improve engine performance and fuel efficiency. Additionally, the butane-based fuel additives are increasingly used to reduce emissions in automotive engines. As governments worldwide push for cleaner and more sustainable fuel solutions, the demand for cleaner butane-based additives is expected to increase.
4. Refrigeration Industry
Butane is also used as a refrigerant in cooling systems, especially in smaller refrigerators and air conditioning units. As an eco-friendly refrigerant alternative to chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), butane’s demand is growing in line with the shift toward sustainable refrigeration technologies.
5. Pharmaceutical Industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, butane is utilized as a propellant in aerosol products such as inhalers, sprays, and perfumes. It is favored in pharmaceutical applications due to its low toxicity and relatively stable nature.
Key Considerations for Establishing a Butane Manufacturing Plant
1. Location Selection
When setting up a butane manufacturing plant, the choice of location plays a significant role in optimizing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Key factors to consider include:
-
Proximity to Raw Material Suppliers: Butane is primarily derived from natural gas or crude oil through processes like cracking. It is essential to locate the plant near suppliers of these raw materials to reduce transportation costs and ensure a reliable supply.
-
Access to Transportation Infrastructure: A well-connected plant will ensure the smooth transportation of raw materials to the facility and the distribution of finished products. Proximity to ports, highways, and railways will be advantageous for logistical purposes.
-
Regulatory Compliance: The plant should be located in an area that meets environmental and safety regulations related to the production and storage of flammable materials such as butane. This includes considering local zoning laws and obtaining the necessary permits for operating a hazardous materials facility.
-
Labor Availability: The selected location should have access to a skilled workforce, including engineers, machine operators, safety personnel, and maintenance staff, to ensure smooth plant operation.
2. Raw Materials and Sourcing
The primary raw material for butane production is natural gas or crude oil. Butane is typically obtained by separating it from natural gas or cracking crude oil during refining. Other raw materials required for butane production may include:
- Catalysts: Specialized catalysts are needed to enhance the cracking process and ensure the effective separation of butane from other hydrocarbons.
- Energy Sources: Butane production requires significant energy input, especially during the separation and refining stages. Reliable access to electricity, steam, and other energy sources is essential.
3. Production Process of Butane
The production process for butane typically involves two main approaches: extraction from natural gas and cracking of crude oil. Below is an outline of the steps involved in each process.
a. Extraction from Natural Gas
In natural gas processing, butane is typically separated from the gas stream using fractionation towers. The raw natural gas is first treated to remove impurities such as sulfur compounds. The remaining gas is then sent through distillation columns to separate it into different hydrocarbon fractions based on their boiling points. Butane, being a heavier hydrocarbon, is separated from lighter gases such as methane and ethane.
b. Cracking of Crude Oil
Crude oil is subjected to a process known as catalytic cracking, where it is heated in the presence of a catalyst to break down complex hydrocarbons into simpler ones. This process generates several by-products, including butane, propane, and gasoline. The butane is then separated from the other by-products through distillation.
4. Purification
After butane is separated from other hydrocarbons, it often requires purification to remove impurities and contaminants. This can be achieved through adsorption or absorption processes, depending on the level of purity required for the intended applications.
5. Storage and Packaging
Butane is a highly flammable substance, so it must be stored in specialized storage tanks that are equipped to handle pressure and prevent leaks. It is typically stored in liquefied form under high pressure or at low temperatures. Packaging and distribution of butane are usually carried out in pressurized cylinders or tankers for bulk distribution.
6. Safety Measures
Due to the highly flammable nature of butane, safety protocols must be strictly followed throughout the production, storage, and transportation processes. Key safety measures include:
- Explosion-proof equipment: The plant must be equipped with explosion-proof machinery and systems to minimize the risk of fire or explosions.
- Leak detection: Continuous monitoring systems should be installed to detect any gas leaks and activate emergency shutdown protocols if necessary.
- Fire suppression systems: Automatic fire detection and suppression systems should be in place to quickly respond to any incidents.
7. Required Equipment for Butane Manufacturing Plant
The following equipment will be necessary to set up a butane manufacturing plant:
- Cracking Units: For breaking down crude oil and natural gas to produce butane.
- Fractionation Towers: For separating butane from other hydrocarbons.
- Distillation Columns: For purifying butane.
- Storage Tanks: To safely store butane under pressure or in liquid form.
- Packaging and Distribution Systems: For filling butane into pressurized cylinders and tankers for transportation.
8. Workforce Requirements
A skilled workforce is essential to operate the butane manufacturing plant. The required personnel may include:
- Production Managers: Oversee the entire production process, ensuring that operations are efficient and meet quality standards.
- Machine Operators: Operate equipment such as cracking units, distillation columns, and storage systems.
- Safety Officers: Ensure compliance with safety protocols and respond to emergencies.
- Maintenance Technicians: Maintain and repair plant machinery to ensure smooth operations.
- Quality Control Inspectors: Monitor product quality to ensure that the butane produced meets industry standards.
9. Environmental and Safety Considerations
Given the hazardous nature of butane, it is essential to adhere to strict environmental and safety guidelines. The facility should implement the following measures:
- Emission Control: Install systems to reduce the emission of harmful gases such as methane and carbon monoxide.
- Waste Management: Properly manage waste materials from the production process to minimize environmental impact.
- Worker Safety: Implement regular training sessions for employees to ensure they are aware of safety measures and emergency procedures.
10. Financial Feasibility and Investment Analysis
Setting up a butane manufacturing plant requires a significant capital investment. Key financial considerations include:
- Initial Investment: The costs associated with land acquisition, construction, machinery, and equipment.
- Operating Costs: Recurring expenses, including raw material procurement, labor, energy consumption, and maintenance.
- Revenue Generation: Income from the sale of butane to various industries, including fuel suppliers, chemical manufacturers, and refrigerant producers.
- Profitability: The expected return on investment (ROI), break-even analysis, and long-term profitability of the plant.
Media Contact
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au