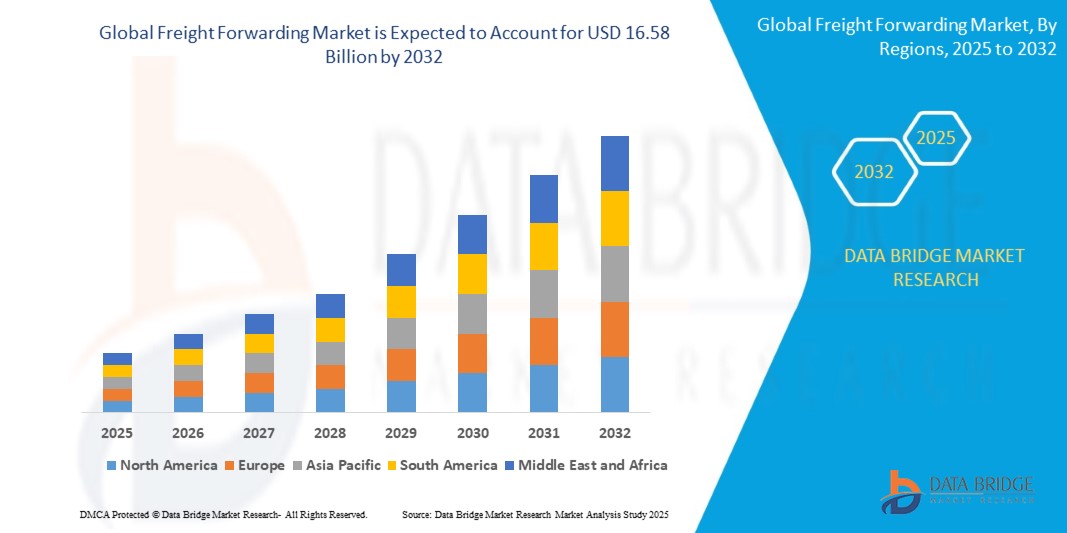
Introduction
The Freight Forwarding Market plays a vital role in global trade, ensuring the smooth movement of goods across borders. As international trade continues to grow, the need for efficient and reliable freight forwarding services has become more critical than ever. From manufacturers to e-commerce businesses, companies worldwide rely on freight forwarders to manage their shipments, navigate customs, and optimize supply chain operations.
The industry has evolved significantly over the years, with technology-driven solutions improving efficiency and transparency. However, challenges such as fluctuating fuel costs, regulatory complexities, and supply chain disruptions pose hurdles for market players. This article explores the current trends, challenges, and future opportunities in the freight forwarding industry.
Understanding Freight Forwarding
What is Freight Forwarding?
Freight forwarding is the coordination and shipment of goods from one location to another through various modes of transportation. Unlike carriers, freight forwarders do not move the goods themselves but act as intermediaries between shippers and transportation services, handling logistics, documentation, and compliance.
Key Functions and Responsibilities of Freight Forwarders
- Cargo Booking & Transportation Coordination – Arranging transport via air, sea, land, or rail.
- Customs Clearance & Regulatory Compliance – Managing tariffs, duties, and paperwork.
- Warehousing & Storage Solutions – Providing temporary storage before shipment.
- Freight Consolidation & Deconsolidation – Combining multiple shipments for cost efficiency.
- Risk Management & Cargo Insurance – Ensuring goods are protected during transit.
Types of Freight Forwarding
- Air Freight – Fast and suitable for high-value or time-sensitive shipments.
- Ocean Freight – Cost-effective for bulk cargo but slower in transit.
- Rail Freight – Efficient for cross-border and long-haul transport.
- Road Freight – Essential for domestic and last-mile deliveries.
- Multimodal Transport – Combining multiple transport modes for optimized logistics.
Market Dynamics and Growth Drivers
Several factors are fueling the growth of the global freight forwarding market:
- Globalization and International Trade Expansion: The rising demand for global supply chains is increasing the need for efficient freight forwarding services.
- E-Commerce Boom: Online retail growth has intensified the demand for fast and reliable shipping solutions.
- Technological Advancements: AI-driven logistics, blockchain-enabled tracking, and IoT-based monitoring systems are revolutionizing freight forwarding.
Key Market Segments
By Mode of Transport
- Air Freight – High-value, perishable goods.
- Ocean Freight – Bulk shipments, industrial goods.
- Rail Freight – Cross-border trade, heavy cargo.
- Road Freight – Short-haul and last-mile deliveries.
By Service
- Freight Transportation – Managing cargo movement.
- Warehousing – Storage and inventory management.
- Value-Added Services – Packaging, labeling, and cargo tracking.
By End-Use Industry
- Retail & E-Commerce – Driving demand for international shipping.
- Automotive & Manufacturing – Supply chain efficiency is critical.
- Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals – Requires temperature-controlled logistics.
Market Trends and Developments
- Digital Freight Forwarding – Online platforms and AI-based logistics optimization.
- Rise of 3PL and 4PL Services – Companies outsourcing supply chain management.
- Sustainability Initiatives – Adoption of low-carbon transportation solutions.
Challenges in the Freight Forwarding Industry
Despite its rapid growth, the freight forwarding industry faces several challenges that impact efficiency, cost, and profitability.
Rising Fuel Costs and Fluctuating Freight Rates
- Fuel price volatility significantly affects operational costs for freight forwarders.
- Global economic conditions and geopolitical factors influence freight rates.
- Companies must adopt cost-optimization strategies, such as route planning and fuel-efficient transportation.
Trade Regulations, Tariffs, and Customs Complexities
- Regulatory compliance varies across countries, making customs clearance a challenge.
- Frequent changes in trade agreements and tariffs impact global freight flows.
- Documentation errors can lead to delays, fines, or shipment rejections.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Capacity Constraints
- The COVID-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains.
- Port congestion, labor shortages, and weather conditions disrupt shipments.
- Freight forwarders must adopt real-time tracking and risk management strategies.
Major Players in the Freight Forwarding Market
The global freight forwarding market is highly competitive, with several key players dominating different regions.
Key Companies and Market Share
- DHL Global Forwarding – One of the largest freight forwarding companies, offering multimodal transport solutions.
- Kuehne + Nagel – A leader in digital freight solutions and supply chain management.
- DB Schenker – Specializes in air, ocean, and land freight services.
- Expeditors International – Focused on innovative logistics technology.
- UPS Supply Chain Solutions – Providing integrated logistics and freight forwarding.
Strategic Partnerships and Mergers
- Companies are forming alliances to expand service networks and improve logistics efficiency.
- Mergers and acquisitions help enhance technological capabilities and increase market share.
Innovation and Technological Adoption
- Use of blockchain for transparent supply chain management.
- AI-powered predictive analytics for demand forecasting.
- IoT-enabled cargo tracking for real-time shipment monitoring.
Regional Analysis
North America: Growth Trends and Key Players
- The U.S. leads in e-commerce-driven freight forwarding.
- Canada focuses on cross-border trade with the U.S. and Mexico.
- High adoption of AI and digital freight platforms.
Europe: Market Dynamics and Regulatory Impact
- Stringent environmental regulations are pushing green logistics initiatives.
- Brexit’s impact on trade policies and customs procedures.
- The rise of rail freight as a sustainable alternative.
Asia-Pacific: The Fastest-Growing Region
- China dominates global trade and logistics.
- India and Southeast Asia are emerging freight hubs.
- Infrastructure investments are driving freight growth.
Rest of the World: Emerging Markets and Opportunities
- Latin America is expanding trade routes to North America and Europe.
- Africa’s logistics industry is growing with increased foreign investment.
- The Middle East focuses on freight connectivity and smart logistics.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance
Freight forwarding is governed by various international laws and regulations.
International Trade Regulations and Policies
- World Trade Organization (WTO) rules impact international freight operations.
- Customs-Trade Partnership Against Terrorism (C-TPAT) ensures security in supply chains.
- Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) standardize trade agreements.
Customs Clearance Procedures and Challenges
- Automated customs clearance systems are reducing paperwork delays.
- Tariff changes affect shipment costs and trade flows.
- Digitization of customs processes enhances efficiency.
Security Measures and Risk Management in Freight Forwarding
- Use of AI-driven risk assessment tools for cargo security.
- Anti-theft and anti-smuggling measures for high-value goods.
- Compliance with global anti-terrorism and cybersecurity regulations.
Future Outlook and Market Forecast
Expected Market Growth and Revenue Projections
- The global freight forwarding market is expected to surpass $250 billion by 2030.
- Growth will be fueled by cross-border e-commerce and digital transformation.
Emerging Technologies and Their Impact
- AI and Machine Learning will enhance supply chain efficiency.
- Blockchain will improve transparency and reduce fraud.
- Autonomous vehicles and drones may revolutionize last-mile delivery.
Role of Artificial Intelligence and Automation in Freight Forwarding
- AI will predict demand fluctuations and optimize freight routes.
- Automation will reduce paperwork and streamline processes.
- AI-powered chatbots will improve customer service in logistics.
Case Studies: Successful Freight Forwarding Operations
Example 1: E-Commerce-Driven Freight Solutions
- Amazon and Alibaba have revolutionized logistics with automated fulfillment centers.
- Fast shipping options like same-day and next-day delivery drive innovation.
Example 2: Sustainable Logistics Practices in Freight Forwarding
- Maersk and DHL invest in eco-friendly shipping solutions.
- Use of electric trucks and biofuel-powered ships.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Carbon Footprint of Freight Forwarding
- Freight contributes to global CO₂ emissions.
- Governments are implementing stricter emission regulations.
Adoption of Alternative Fuels and Eco-Friendly Logistics Solutions
- Companies are shifting to LNG-powered ships and electric delivery trucks.
- Increased investment in green logistics and carbon offset programs.
Regulatory Push Towards Greener Freight Operations
- The IMO’s 2050 decarbonization goals for the shipping industry.
- New policies promoting sustainable supply chain practices.
Investment Opportunities and Market Strategies
Areas of Investment in Freight Forwarding
- Technology-driven logistics solutions.
- Expansion into emerging markets.
- Sustainability-focused freight initiatives.
Strategies for Businesses to Optimize Logistics Operations
- Leveraging AI-powered route optimization to reduce costs.
- Expanding warehousing and fulfillment networks.
- Partnering with digital freight platforms for efficiency.
Competitive Landscape and Business Strategies
Mergers, Acquisitions, and Strategic Alliances
- Companies are merging to expand global reach and service capabilities.
- Strategic partnerships with tech firms are enhancing digital transformation.
Business Models and Pricing Strategies in Freight Forwarding
- Dynamic pricing models based on demand fluctuations.
- Subscription-based logistics services for SMEs.
Challenges in Maintaining Competitive Advantage
- Rising competition from digital freight startups.
- Need for continuous innovation and technology upgrades.
Conclusion
The freight forwarding market is undergoing a major transformation, driven by digitalization, e-commerce, and sustainability efforts. As international trade grows, freight forwarders must adapt to regulatory changes, optimize costs, and invest in cutting-edge technology.
With challenges like fuel price fluctuations, customs complexities, and supply chain disruptions, freight companies must focus on efficiency, transparency, and sustainability. The future of freight forwarding lies in automation, AI-driven logistics, and eco-friendly transportation solutions.
Get More Details : https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-freight-forwarding-market